Trouble today with my Jeep Liberty
first code P0301 and P0306 and the P0300
Found the definition of the code and Luckely not the head gasket.
I drove the car home on 4 cylinders and took the other car.
When I came home at the end of the day I tried again the car and there was no problem. Just the codes which I read through OBD2 with Torque (app)
I will check tomorrow my spark plugs and wiring. I hope I can find something, because then I can solve it.
Everything else in the list was;
P0301 JEEP Possible Causes
What does this mean?
- Faulty spark plug 1
- Clogged or faulty fuel injector 1
- Faulty ignition coil 1
- Fuel injector 1 harness is open or shorted
- Fuel injector 1 circuit poor electrical connection
- Ignition coil 1 harness is open or shorted
- Ignition coil 1 circuit poor electrical connection
- Insufficient cylinder 1 compression
- Incorrect fuel pressure
- Intake air leak
So will check all the electrical as well.
Hope that I wont have that problem again.
Unfortunately, I could not find any more information about this DTC than you already did without having the car here.
P0301 means: Misfire Cly.1
P0306 means: Misfire Cyl.6
P0300 means: Multiple Cly. Misfires
When were the spar plugs changed? Maybe you can check this:
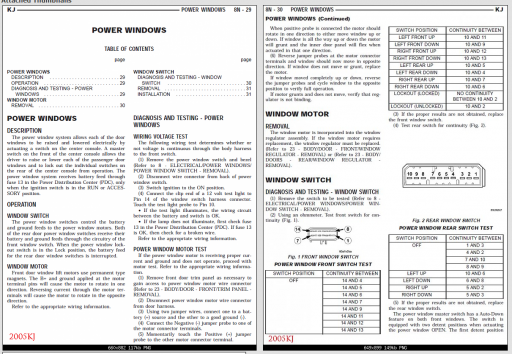
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 3.7L V-6
PRIMARY RESISTANCE 21-27°C (70-80°F) 0.6 - 0.9 Ohms
SECONDARY RESISTANCE 21-27°C (70-80°F) 6,000 - 9,000 Ohms
ENGINE PLUG TYPE ELECTRODE GAP
3.7L V-6 2FR6F - 11G (NGK #) 1.1 mm (0.042 in.)
3.7L Battery voltage is supplied to the 6 ignition coils from the ASD relay. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) opens and closes each ignition coil ground circuit at a determined time for ignition coil operation. Base ignition timing is not adjustable. By controlling the coil ground circuit, the PCM is able to set the base timing and adjust the ignition timing advance. This is done to meet changing engine operating conditions. The ignition coil is not oil filled. The windings are embedded in an epoxy compound. This provides heat and vibration resistance that allows the ignition coil to be mounted on the engine. Because of coil design, spark plug cables (secondary cables) are not used with the 3.7L engine.
An individual ignition coil is used for each spark plug (Fig. 19). The coil fits into machined holes in the cylinder head. A mounting stud/nut secures each coil to the top of the intake manifold (Fig. 18). The bottom of the coil is equipped with a rubber boot to seal the spark plug to the coil. Inside each rubber boot is a spring. The spring is used for a mechanical contact between the coil and the top of the spark plug. These rubber boots and springs are a permanent part of the coil and are not serviced separately.
An o-ring (Fig. 19) is used to seal the coil at the opening into the cylinder head. (1) Depending on which coil is being removed, the throttle body air intake tube or intake box may need to be removed to gain access to coil. (2) Disconnect electrical connector from coil by pushing downward on release lock on top of connector and pull connector from coil. (3) Clean area at base of coil with compressed air before removal. (4) Remove coil mounting nut from mounting stud (Fig. 18). (5) Carefully pull up coil from cylinder head opening with a slight twisting action. (6) Remove coil from vehicle.
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR DESCRIPTION One coil capacitor is used. It is located in the engine compartment and attached (clipped) to a wiring trough near the brake power booster. OPERATION The coil capacitor(s) help dampen the amount of conducted electrical noise to the camshaft position sensor, crankshaft position sensor, and throttle position sensor. This noise is generated on the 12V supply wire to the ignition coils and fuel injectors. REMOVAL The coil capacitor is located in the engine compartment and is attached (clipped) to a wiring harness trough near the brake power booster (graphic not available). (1) Unclip capacitor from wiring harness trough. (2) Disconnect electrical connector at capacitor. INSTALLATION (1) Connect electrical connector to coil capacitor. (2) Position capacitor into v-clip on wiring harness trough.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR DESCRIPTION The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is mounted in the top of cylinder head cover/intake manifold at the rear of the engine (Fig. 1) (Fig. 2) The CMP sensor is a hall effect device. OPERATION The CMP sensor is a hall effect switch. A tooth made of a ferromagnetic material is attached to the camshaft. When this tooth passes the CMP sensor an lectronic signal is created. This signal is then sent to the engine control module (ECM). This signal is used by the ECM to determine which cylinder has just entered its compression phase.
Maybe you can check first all plugs and check if every O-ring sealing is okay ( cause you said there was water in it ).-
Best regards
Tobias